INTRODUCTION
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major and growing public health problem worldwide, with a 9% annual increase in numbers of patients. Moreover, CKD is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and other systemic complications.[1] Its main causes in developed countries—and many developing countries—are diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure, but glomerulonephritis and CKD of unknown causes are more common in Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa and Central America.[2–7]
Epidemiologic studies put global CKD prevalence at approximately 7.2% in the population aged >30 years and 23.4% to 35.8% in people aged >64 years.[7] However, the figures vary from country to country: the EPIRCE study in Spain reported a 3.3% prevalence of chronic renal failure (CRF: CKD stages 3a, 3b, 4 and 5) in those aged 40–64 years and 21.4% in those aged >64 years.[8] In China, estimated CKD prevalence is 10.8%.[9] A study of an at-risk population in an Australian community reported a 20.4% prevalence, with an even higher figure for people aged ≥61 years.[10] These studies, moreover, reported various risk factors, such as age >60 years, smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, cardiovascular disease, hypertension (HT), diabetes, and low socioeconomic status.[7–10]
In 2010 in the USA 594,374 patients received renal replacement therapy, either dialysis or transplantation, resulting in a rate of 340 per million population (pmp); that same year, spending in the country on CKD reached $47.5 billion.[11] In 2011, the United Kingdom reported 53,207 (856 pmp) adults with CKD, a 4% increase over 2010.[12]
The global increase in CKD burden is attributable to two major factors: rising incidence caused by the global diabetes epidemic on the one hand, as well as population aging. In developing countries, the number of diabetes patients is expected to soar from 99 million in 1995 to 286 million by 2025.[13,14]
Various studies have been conducted in Latin America and the Caribbean, but country data are incomplete. Estimates by the Latin American Dialysis and Transplant Registry in 2008 put total patients in all stages of CKD at 47 million; it also reported prevalence of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) had risen from 199 pmp in 1991 to 568 pmp in 2008, with ESRD incidence increasing to 207.6 pmp. This increase in disease burden is due mainly to the epidemiologic transition, an increase in number of diabetes cases, and better CKD detection because of wider access to health services, although comprehensive health coverage is not available in all countries. CKD risk factors and renal damage markers identified included low income, type 2 diabetes, HT, hematuria, proteinuria, and elevated serum creatinine.[15,16] In Mexico, the KEEP-México and KEEP-Jalisco studies targeting CKD at-risk populations (patients with HT, type 2 diabetes and a family history of CKD) reported prevalences of 22% and 33%, in Mexico City and Jalisco, respectively. Researchers also found that diabetes and HT, coupled with overweight, were the most important CKD risk factors.[17]
In El Salvador, CKD is an increasingly important public health problem. Ministry of Health (MINSAL, the Spanish acronym) data for 2011 point to CRF as the leading cause of hospital deaths in adult men, with CKD the overall leading cause of death reported since 2009.[18] Since 2002, El Salvador records a high prevalence of CKD unassociated with diabetes or hypertension, affecting mainly young male farm workers who performed strenuous labor and reported high levels of exposure to agrochemicals.[5] Other publications in Central America have also called attention to this phenomenon.[6,15,19–22]
Since 2009, several studies on CKD of nontraditional causes have been conducted in El Salvador. Orantes found CKD prevalence of 17.9% and CRF prevalence of 9.8% in the population aged >18 years in Bajo Lempa (an agricultural region in the Lempa river delta), and identified multiple traditional and nontraditional risk factors, chiefly farm labor and exposure to agrochemicals, to consider in future research.[4] Other studies in the same region reported environmental pollution with heavy metals such as arsenic, possibly associated with use of agrochemicals, worse in groundwater and areas under cultivation.[22]
The present study was conducted in 2012 in two farming communities in different parts of the country, to further elucidate the reported association between CKD from nontraditional causes and poverty, farm labor and environmental pollution, all of which may contribute to the development of the disease. These communities are at the same altitude (300 m), but cultivate different crops. The main crop in the first, El Jícaro, is corn; in the second, Dimas Rodríguez, subsistence farming and other crops, such as beans. The purpose of this study was to determine the prevalence of CKD and its risk factors in the population aged ≥15 years in the two communities.
METHODS
A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted by the Renal Health Research Unit of MINSAL’s National Institute of Health in two farming communities: El Jícaro (San Agustín municipality, department of Usulután) and Dimas Rodríguez (El Paisnal municipality, department of San Salvador). From March through September 2012, investigators used epidemiological and clinical methods to actively screen for CKD and its risk factors in the resident population aged >15 years. The population universe was 244: 136 in El Jícaro and 108 in Dimas Rodríguez; 223 individuals (91.4%) were studied. The study was conducted in three phases:
- Active search for CKD cases and risk factors
- Detection of urinary and blood markers for kidney disease
- Estimation of kidney function using mathematical equations found in the KDIGO 2012 guidelines (CKD–EPI in adults and Schwartz in adolescents)[23–25]
The study algorithm in Figure 1 includes case criteria for CKD.
Variables See Table 1.
Procedures Each participant was assigned a record number and code for clinical monitoring during the study. Trained health workers interviewed participants to collect information on personal and family medical history, and occupational and environmental risks; take physical measurements (including height, weight and abdominal circumference), and blood pressure. A first morning urine sample was analyzed, using 10-parameter reactive strips and reactive strips for determining albumen/creatinine ratio with the URISYS automated strip reader (Roche Diagnostics, Germany). A fasting venous blood sample was taken to determine biochemical parameters such as creatinine (Trinder enzymatic reaction), fasting glucose, cholesterol and triglycerides. Samples were processed at a clinical laboratory installed in each study community and equipped with a spectrophotometer and its respective reagents (SPINREACT, Spain). All instruments were calibrated to guarantee sample quality and reliability. Laboratory tests were done according to manufacturer’s instructions, with their respective controls. Data from the paper questionnaires were digitalized using Visual Basic software.
Figure 1: Study algorithm
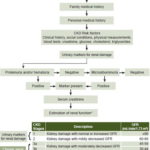
CKD: chronic kidney disease GRF: glomerular filtration rate * CKD–EPI in adults, Schwartz in adolescents[23–25]
Ethics Written informed consent was obtained from all participants, and from parents or guardians of minors. Participants agreed to publication of findings providing confidentiality was respected. Those diagnosed with medical conditions received followup from their community family health units.
Figure 1: Study variables
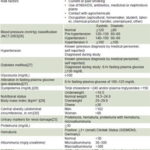
BSA: body surface area CKD: chronic kidney disease GFR: glomerular filtration rate HT: hypertension
RESULTS
The average age of the study population was 35.1 years in El Jícaro and 34 years in Dimas Rodríguez, with those aged >60 years accounting for 10.8% of the total study population. Risk factor prevalences by sex and community are presented in Table 2.
A first-degree family history of CKD was reported by 12.6% of participants, diabetes by 20.2% and HT by 28.3%. Personal history of CKD was reported by 9.4% of participants in El Jícaro and 10.5% in Dimas Rodríguez.
No participant in either community reported having diabetic or hypertensive kidney disease or receiving renal replacement therapy. History of prior infectious diseases such as intestinal parasites, chicken pox, and tonsillitis was reported more often in Dimas Rodríguez (87.4% vs. 35.2% in El Jícaro) (Table 2).
Current alcohol and tobacco use were more prevalent in Dimas Rodríguez than El Jícaro (36.8% vs. 24.2% and 28.4% vs. 18%, respectively), as were use of medicinal plants (69.5% vs. 46.1%) and NSAIDs (77.9% vs. 61.7%). The most commonly used NSAIDs were ibuprofen (22.0%), aspirin (8.5%) and diclofenac (8.3%). There were no reports of nephrotoxic plant consumption, such as starfruit.
Some 94.5% of men reported contact with agrochemicals and 59.3% of women, and 96.4% of men and 54.9% of women were farmworkers. In the medical interviews, the research team learned that nine products were responsible for agrochemical exposure in farming. The most frequently used in El Jícaro were the herbicide dipyridlium (paraquat), a phenoxyacetic acid herbicide (2,4-D), and an aminophosphonate herbicide (glyphosate). In Dimas Rodríguez, paraquat, 2,4-D, and the organophosphate methyl parathion were used most often.
HT prevalence was 10.9% in El Jícaro and 8.4% in Dimas Rodríguez. Diabetes prevalence was higher in Dimas Rodríguez (9.5%) than in El Jícaro (2.3%). However, 91.1% (102/112) of participants with CKD had no history or evidence of diabetes, and 76.9% (86) had neither diabetes nor HT. The most prominent lipid disorder was high serum triglycerides, 55.5% in El Jícaro and 29.5% in Dimas Rodríguez. There was a high prevalence of overweight, 30.5% in both communities, and obesity (El Jícaro, 18%; Dimas Rodríguez, 12.6%), particularly in women (Table 2).
Renal damage markers were detected in 30.9% of the population studied, with a much higher frequency in El Jícaro than in Dimas Rodríguez (47.7% vs. 8.4%). In both communities, there was a higher prevalence of positive urinary markers for renal damage in men. The most common marker was microalbuminuria (18.8% in the total population). Estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) progressively declined with age in both sexes throughout the age span studied. In the group aged 50–59 years, average GFR was 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, the threshold for CRF (Figure 2).
Table 2: Prevalence of CKD risk factors in two Salvadoran farming communities (n = 223)

CKD: chronic kidney disease
Figure 2: Estimated GFR in two Salvadoran farming communities by sex and age group
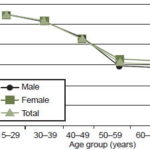
GFR: glomerular filtration rate
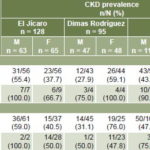
Overall CKD prevalence in the study population was 50.2% (112/223); in El Jícaro 52.3% (men 60.3%; women 44.6%) and in Dimas Rodríguez, 47.4% (men 31.9%, women: 62.5%). The largest number of cases was in the 15–59-year age group in both communities, but CKD prevalence was higher in the older group; similarly, the largest number of cases was in farmworkers, but prevalence was similar between farmworkers and nonfarmworkers (Table 3). Prevalence of stage 1 CKD was 35.2% in El Jícaro and 0% in Dimas Rodríguez, while stage 2 prevalence was similar in the two communities: 8.6% El Jícaro and 8.4% in Dimas Rodríguez. Overall CRF prevalence was 16.1% (36 people), 10.9% in men and 21.2% in women. The M:F ratio for CRF was 2.7 in El Jícaro and 0.19 in Dimas Rodríguez. Only in El Jícaro were patients in stages 4 and 5 found (0.7% and 2.3%, respectively).
DISCUSSION
The sociodemographic characteristics of the communities studied are typical of rural El Salvador, with a relatively young population whose primary source of income is agriculture.[31] Several risk factors for CKD are part of this social context: high prevalence of CKD family history, diabetes and HT, suggesting possible hereditary susceptibility or predisposing environmental factors. Our study findings in this respect are comparable to those of another study conducted in a rural community on the Salvadoran coast, which found prevalences of the aforementioned factors of 21.6%, 22.9% and 40.3% respectively.[4] In México, however, the KEEP-México and KEEP-Jalisco studies reported higher prevalence associated with family history of CKD (52%) but prevalence of diabetes and HT together similar to those found in our study (23%).[17]
Alcohol consumption was high, especially among men. Researchers in Nicaragua have posited an association between development of CKD from nontraditional causes and consumption of homemade alcoholic beverages,[20] but to date, there are no studies supporting that hypothesis. Prevalence of smoking and previous smoking was higher in men in both communities; similar findings have been reported in other Salvadoran farming communities (13.8%, 17.3% respectively)[4] and in a study of a rural community in Mexico (smoking prevalence 14.9%).[32] Although NSAID use was the third most frequent risk factor reported, duration of exposure to these nephrotoxic drugs could not be measured, because of the cross-sectional nature of the study. All these risk factors are common to both sexes in both communities. Nephrotoxic plants did not figure among the medicinal plants used by study participants.[33–35]
Table 3: CKD prevalence in two Salvadoran farming communities by sex, age and occupation (n = 223)
Participant reports of using agricultural chemicals with no protective gear and of long hours of strenuous labor under the sun are consistent with observations in other farming communities in El Salvador, where occupational exposure to agrochemicals and poor occupational hygiene appear to be a common factor.[19,21] The 2009 Nefrolempa study reported that more than half the study population was exposed to agrochemicals and more than 80% of men used these products.[4]
HT prevalence observed was also lower than that reported in the studies cited: Australia 38%–51%;[10] USA 29%;[36] Spain 24.1%;[8] and Nefrolempa 16%.[5] The study found a lower diabetes prevalence than that reported in other international studies: Australia 15%;[10] USA 10.3%;[36] Spain 9.2%;[8] Mexico 9.2%;[37] and Nefrolempa 10.3%.[4]
The high prevalences of overweight and obesity we observed, especially among women, are similar to those of other studies in El Salvador (34% and 22.4%, respectively),[4] Spain (39.4% and 26.1%, respectively)[8] and USA, in which only overweight is similar (34.8% and 30.8%, respectively).[36]
For the majority of traditional and nontraditional risk factors for CKD found in this study and reported by other investigators, the figures for men were higher.[4] Nicaragua has seen an increase in the number of CKD patients with the same epidemiologic characteristics: male farm workers aged <60 years exposed to pesticides and dehydration.[20] Studies in Sri Lanka have shown a strong association between use of agrochemicals, heavy metals, and CKD from nontraditional causes.[38] In Guanacaste, Costa Rica, an increase in CKD cases, especially interstitial nephritis, has been observed in sugarcane workers.[6,39]
CKD and CRF prevalence in the study population was high and in most cases, patients did not have traditional CKD risk factors. What was most striking was the disease’s high prevalence in younger people. Some gender differences between the communities were observed, with a higher prevalence of CKD in women in the Dimas Rodríguez community. This study needs to be complemented with other environmental studies that furnish better evidence to determine whether there are gender-related or occupational differences in exposure to pollutants.
Among the constraints of this study were the facts that CKD cases defined by urinary renal damage markers could not be confirmed, and that mathematical formulas for calculating GFR developed for other populations may not be appropriate for this one.
Lack of detail on quantity and duration of use of some substances (notably NSAIDs, the most frequently reported) limits inference from prevalences found. Also, because the study population was small, we did not do in-depth statistical analysis, including tests of association and confidence intervals for prevalences. Notwithstanding, the study establishes the scope of the CKD problem in these communities and can provide further contextualization for causal hypotheses and potential risk factors.
CONCLUSIONS
CKD prevalence is alarming in these communities, among both young and old, men and women, independently of occupation. Health services must cope with the increased CKD burden observed, and are challenged to implement preventive strategies.








